Ancient Israel is entwined with the land and history of Palestine. No other land in the world is so firmly entrenched in a country’s history as Palestine is in Israel’s.
In fact, ancient Palestine, also referred to as Canaan, or Israel, has come to be known as the Holy Land.
However, the history of this land is anything but holy. Some of the world’s oldest and most powerful empires have left bloody footprints in Palestine.
Ancient Near East
Ancient Mesopotamia: Ancient Mesopotamia and the history of Palestine are entwined with each other even before the Bible. Abraham migrated from ancient Mesopotamia.
Ancient Egypt Geography: Ancient Egypt geography led Egypt to seek control of routes leading to the east. Thus, the country often came into conflict with Palestine and Israel.
Ancient Syria: Palestine and Syria shared much more than geographical location. The two countries fought each other frequently in the Old Testament.
Cedars of Lebanon: The cedars of Lebanon were the most sought after timber in the ancient world. Kings and Pharaohs sought after this precious resource. Consequently it played a significant role in ancient Lebanon’s economy and culture.
Pre Biblical Ancient Palestine
The rich history of ancient Palestine extends back thousands of years before Abraham set foot in Canaan. Canaanite culture was well developed, consisting of complex relations and loyalties.
Maps of Palestine from ancient times to the present day. The tribes of Israel are given in detail, as well as the many geographical features of the land.
The Ancient Near East was dominated by two major powers, Egypt and Mesopotamia. Palestine was caught in the middle of these two great empires.
Consequently, the history of Canaan was largely shaped by these two powers.
This small strip of land was greatly influenced by the presence of these two empires. Palestine was essentially a land bridge between them.
The International Coastal Highway also ran through Palestine, providing important and vital links to trade, commerce, culture, etc.
Accordingly, Palestine’s strategic importance was not lost on either empire, as they often struggled for control over her important trade and military routes.
The people of Palestine, thus, felt the imprint of many different cultures and religions. The people were influenced significantly by this diversity.
They also felt the brunt of war. Empires waged war over the important trade routes in Palestine, and sought to control this strategically located little stretch of land.
As a result, the history of Palestine is marred by countless bloody conflicts.
Empires such as the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Romans, waged wars to control the strategically important area, and to put down rebellions.
Conditions were also very favorable to agriculture in most of the Ancient Near East. The term, The Fertile Crescent, was coined to describe this region and its early agricultural settlements, which would eventually lead to village life.
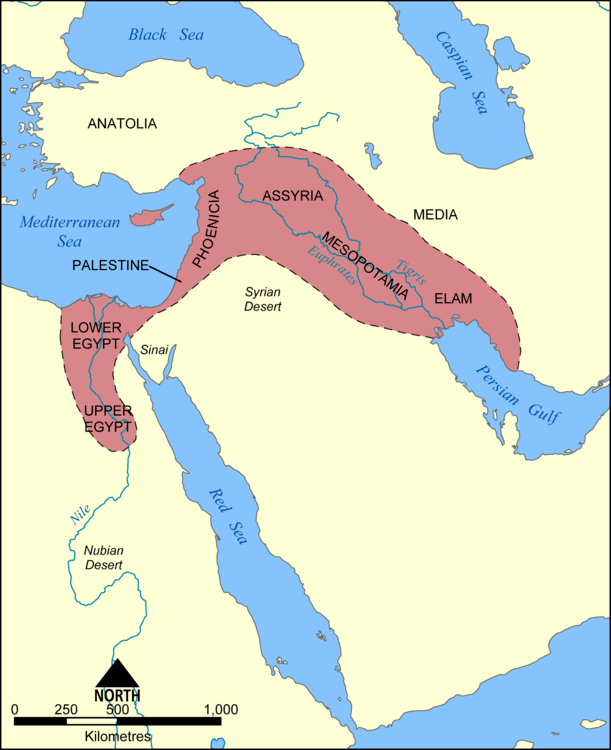
The Fertile Crescent starts in the Persian Gulf, near modern day Basra. From the gulf it stretches northwest into Mesopotamia, which included the lands bordering the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
From there, it runs into southern Turkey, encompassing modern day cities such as Diyarbekir, Samsat, and Gaziantep.
In southern Turkey, The Fertile Crescent bends southward, and runs along the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea.
The Crescent then makes its way southward down the coast to Israel, where it collides with the Negeb, and abruptly ends.
Sandwiched between the eastern coast of the Mediterranean and the desert is a thin line of country known as the Levant.
Syria formed the northern border of the Levant, while Palestine occupied the southern portion of the Levant.
Southwards of the Levant is the Negeb, leading across the Sinai peninsula into Egypt. Many of Israel’s Patriarchs and heroes have traversed the Negeb throughout the history of Palestine.
East of the Levant is the Syro-Arabian desert. On the other side of the Syro-Arabian desert is Babylon, or, Mesopotamia. West of the Levant is the Mediterranean Sea, leading to Greece, Italy and Rome.
The geography of the land also played an extremely significant part in the history of Palestine.
Study Resource
Barnesandnoble.com offers The History of Ancient Palestine. This book encompasses the history of Palestine from the earliest times to Alexander’s conquest. It draws on all available material including archeological excavations from the ancient Near East. Click on the link below to obtain your copy of The History of Ancient Palestine!



